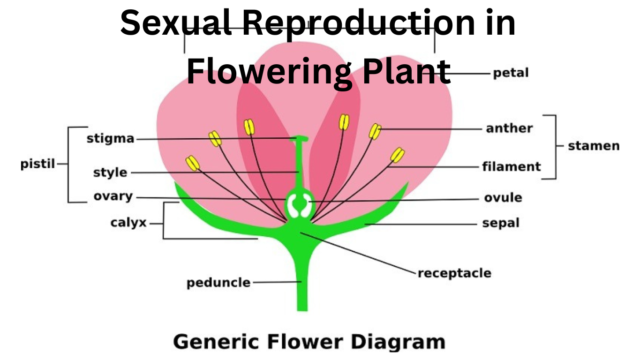
MULTIPLE CHOICE QUESTION NCERT
- Among the terms listed below, those that of are not technically correct names for a floral whorl are:
(i) Androecium
(ii) Carpel
(iii) Corolla
(iv) Sepal
(a) (i) and (iv)
(b) (iii) and (iv)
(c) (ii) and (iv)
(d) (i) and (ii)
ANSWER – ——–
- Embryo sac is to ovule as ————- is to an anther:
(a) Stamen
(b) Filament
(c) Pollen grain
(d) Androecium
ANSWER – ——–
- In a typical complete, bisexual and hypogynous flower, the arrangement of floral whorls on the thalamus from the outermost to the innermost is:
(a) Calyx, corolla, androecium and gynoecium
(b) Calyx, corolla, gynoecium and androecium
(c) Gynoecium, androecium, corolla and calyx
(d) Androecium, gynoecium, corolla and calyx
ANSWER – ——–
- A Dicotyledonous plant bears flowers but never produces fruits and seeds. The most probable cause for the above situation is:
(a) Plant is dioecious and bears only pistillate flowers
(b) Plant is dioecious and bears both pistillate and staminate flowers
(c) Plant is monoecious
(d) Plant is dioecious and bears only staminate flowers.
ANSWER – ——–
- The outermost and innermost wall layers of microsporangium in an anther are respectively:
(a) Endothecium and tapetum
(b) Epidermis and endodermis
(c) Epidermis and middle layer
(d) Epidermis and tapetum
ANSWER – ——–
- During microsporogenesis, meiosis occurs in:
(a) Endothecium
(b) Microspore mother cells
(c) Microspore tetrads
(d) Pollen grains
ANSWER – ——–
- From among the sets of terms given below, identify those that are associated with the gynoecium:
(a) Stigma, ovule, embryo sac, placenta
(b) Thalamus, pistil, style, ovule
(c) Ovule, ovary, embryo sac, tapetum
(d) Ovule, stamen, ovary, embryo sac
ANSWER – ——–
- Starting from the innermost part, the correct sequence of parts in an ovule are:
(a) Egg, nucellus, embryo sac, integument
(b) Egg, embryo sac, nucellus, integument
(c) Embryo sac, nucellus, integument, egg
(d) Egg, integument, embryo sac, nucellus.
ANSWER – ——–
- From the statements given below choose the option that are true for a typical female gametophyte of a flowering plant:
(i) It is 8-nucleate and 7-celled at maturity
(ii) It is free-nuclear during the development
(iii) It is situated inside the integument but outside the nucellus
(iv) It has an egg apparatus situated at the chalazal end
(a) (i) and (iv)
(b) (ii) and (iii)
(c) (i) and (ii)
(d) (ii) and (iv)
ANSWER – ——–
- Autogamy can occur in a chasmogamous flower if:
(a) Pollen matures before maturity of ovule
(b) Ovules mature before maturity of pollen
(c) Both pollen and ovules mature simultaneously
(d) Both anther and stigma are of equal lengths.
ANSWER – ——–
- Choose the correct statement from the following:
(a) Cleistogamous flowers always exhibit autogamy
(b) Chasmogamous flowers always exhibit geitonogamy
(c) Cleistogamous flowers exhibit both autogamy and geitonogamy
(d) Chasmogamous flowers never exhibit autogamy
ANSWER – ——–
- A particular species of plant produces light, non-sticky pollen in large numbers and its stigmas are long and feathery. These modifications facilitate pollination by:
(a) Insects
(b) Water
(c) Wind
(d) Animals
ANSWER – ——–
- From among the situations given below, choose the one that prevents both autogamy and geitonogamy:
(a) Monoecious plant bearing unisexual flowers
(b) Dioecious plant bearing only male or female flowers
(c) Monoecious plant with bisexual flowers (
(d) Dioecious plant with bisexual flowers
ANSWER – ——–
- In a fertilised embryo sac, the haploid, diploid and triploid structures are:
(a) Synergid, zygote and primary endosperm nucleus
(b) Synergid, antipodal and polar nuclei
(c) Antipodal, synergid and primary endosperm nucleus
(d) Synergid, polar nuclei and zygote.
ANSWER – ——–
- In an embryo sac, the cells that degenerate after fertilisation are:
(a) Synergids and primary endosperm cell
(b) Synergids and antipodals
(c) Antipodals and primary endosperm cell
(d) Egg and antipodals.
ANSWER – ——–
16 . While planning for an artificial hybridization programme involving dioecious Plants, which of the following steps would not be relevant:
(a) Bagging of female flower
(b) Dusting of pollen on stigma
(c) Emasculation
(d) Collection of pollen
ANSWER – ——–
- In the embryos of a typical dicot and a grass, true homologous structures are:
(a) Coleorhiza and coleoptile
(b) Coleoptile and scutellum
(c) Cotyledons and scutellum
(d) Hypocotyl and radicle.
ANSWER – ——–
- The phenomenon observed in some plants wherein parts of the sexual apparatus is used for forming embryos without fertilisation is called:
(a) Parthenocarpy
(b) Apomixis
.(c) Vegetative propagation
(d) Sexual Reproduction
ANSWER – ——–
- In a flower, if the megaspore mother cell forms megaspores without undergoing meiosis and if one of the megaspores develops into an embryo sac, its nuclei would be:
(a) Haploid
(b) Diploid
(c) A few haploid and a few diploid
(d) With varying ploidy
ANSWER – ——–
- The phenomenon wherein, the ovary develops into a fruit without fertilisation is called:
(a) Parthenocarpy
(b) Apomixis
(c) Asexual reproduction
(d) Sexual reproduction
ANSWER – ——–
21. In some plants, anthers and stigma grow and mature at same time. This phenomenon is called:
(a) Homogamy
(b) Syngamy
(c) Allogamy
(d) Fusion
ANSWER – ——–
22. Which one of the following is surrounded by a callose wall?
(a) Male gamete
(b) Egg
(c) Pollen grain
(d) Microspore mother cell
ANSWER – ——–
23. Male gametes in angiosperms are formed by the division of:
(a) Microspore mother cell
(b) Microspore
(c) Generative cell
(d) Vegetative cell requires
ANSWER – ——–
24. Double fertilization (or triple fusion) leading to initiation of endosperm in angiosperms,
(a) Fusion of 4 or more polar nuclei and the second male gamete only
(b) Fusion of 2 polar nuclei and second male gamete only
(c) Fusion of one polar nucleus and second male gamete only
(d) All the above types of fusions in different types of angiosperms
ANSWER – ——–
25. Eight nucleate embryo sacs are:
(a) Always bisporic
(b) Always tetrasporic
(c) Always monosporic
(d) Sometimes monosporic, sometimes bisporic and sometimes tetrasporic
ANSWER – ——–
26. Triploid tissue in angiosperms is:
(a) Nucellus
(b) Endosperm
(c) Endomitosis
(d) Tapetum
ANSWER – ——–
27. Tapetal cells are characterised by:
(a) Mitotic division
(b) Meiotic division
(c) Endothecium
(d) Endomitosis as well as endopolyploidy
ANSWER – ——–
28. Anemophily type of pollination is found in:
(a) Salvia
(b) Bottle brush
(c) Vallisneria
(d) Coconut
ANSWER – ——–
29. The outermost layer of maize endosperm is known as:
(a) Perisperm
(b) Aleurone
(c) Tapetum
(d) Endothecium
ANSWER – ——–
30. Edible part in mango is:
(a) Endocarp
(b) Receptacle
(c) Epicarp
(d) Mesocarp
ANSWER – ——–
ANSWERSHEET –
| 1. | c | 11 | a | 21 | a |
| 2 | c | 12 | c | 22 | d |
| 3 | a | 13 | b | 23 | c |
| 4 | d | 14 | a | 24 | b |
| 5 | d | 15 | b | 25 | d |
| 6 | b | 16 | c | 26 | b |
| 7 | a | 17 | c | 27 | d |
| 8 | b | 18 | b | 28 | d |
| 9 | c | 19 | b | 29 | b |
| 10 | c | 20 | a | 30 | d |